Cross Flow Heat Exchanger Equations
The primary and secondary fluid in an heat exchanger process may. The heat exchange duty a.
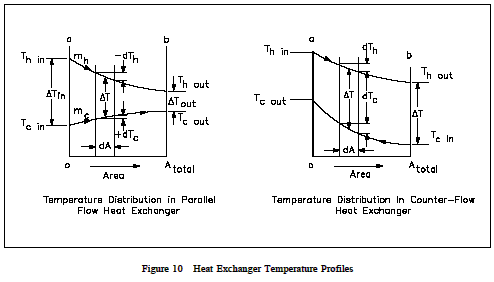
Parallel And Counter Flow Designs Heat Exchangers
Heat exchangers have widespread industrial and.

. It is a measure of the heat exchangers departure from the ideal behavior of a counter flow heat exchanger having the same terminal temperatures. And the thermal conductivity is 012 Btuhr-ft-F. The engine oil at a flow rate of 023 kgs enters the exchanger at 120C and leaves at 115C.
The F-LMTD method is widely used in heat exchanger analysis particularly for heat exchanger selection sizing problems when as a result of the process requirements the temperatures are known and the size of the heat exchanger is. Heat exchanger networks are designed through insightful use of pinch analysis. The pinch point divides the temperature range into two.
A steady fluid flow infers a flow of which parameters such as mass flow rate pressure temperature etc. In parallel flow both fluids move in the same direction while transferring heat. Examples of T-Q diagrams for a parallel flow heat exchanger left and a counter or cross flow heat exchanger middle.
The thickness is 1 in. In the opposite direction - counter-current flow. Model Equations and Heuristics.
When designing or reviewing heat 1600 Flue gas stream exchanger networks the Watersteam stream 1400 T-Q diagram gets useful. Shell and tube heat exchangers are widely used in many different industries 910 such as power plants oil and gas industries and refrigerationTurbulent cross flow and heat transfer in tube bundles is a classical problem of shell and tube heat exchangers and has been investigated by many researchers. This type of flow is suitable for handling low density gas which passes through the cross flow avoiding pressure loss.
Flows of mass and energy that cross the system boundary are steady. Our exceptional CFD simulation software provides CFD meshing solving and post-processing and is compatible with external CFD workflows. Effectiveness-NTU curves for different values of Cr Reference.
The computational world is due for an update to computational methodologies and the update is. 1000 Btuhr is conducted through a section of insulating material shown in Figure 1 that measures 1 ft 2 in cross-sectional area. Mohrs Circle Equation and Calculator.
Engineering 2D and 3D Statics Basics Equations and Calculators. The simplest heat exchanger is one for which the hot and cold fluids move in the same or opposite directions in a concentric tube or double-pipe construction. 𝑐𝑐 ln Parallel-Flow Heat Exchanger 𝑙𝑙𝑚𝑚𝐶𝐶𝑃𝑃 𝑑𝑑.
Example 52 Miniature Shell-and-Tube Heat Exchanger A miniature shell-and-tube heat exchanger is designed to cool engine oil in an engine with the engine coolant 50 ethylene glycol. The mass and energy balance equations of the heat exchanger for air heating are given as. It can be used for liquid-liquid applications if one liquid has a considerably greater flow.
Heat Exchangers Transfer of heat is usually accomplished by means of a device known as a heat exchanger. Given that mass flow rate heat transfer rates and work transfer rates are constant the. The double pipe heat exchanger is one heat exchanger pipe inside another larger pipe for either counter flow or parallel flow pattern.
The hot stream is marked with red color and the cold with blue color. In counter flow the fluids move in opposite directions. One fluid is in spiral flow and the other in a cross flow.
Torsional Deformation and Stress of a Cross Shaft Equations and Calculator. In the counterflow arrangement of Figure 188b the. Ln Counter-Flow Heat Exchanger For Cross-Flow and Shell-and-Tube Heat Exchangers.
Effective incorporation of heat exchanger networks will minimize the use of utilities minimize the number of heat exchangers and minimize costs associated with the design. The 50 ethylene glycol at a rate of 047 kgs enters at 90C. Or perpendicular to each other - cross flow.
Flow in the same direction - parallel flow or co-current flow. Principal and Von-Mises Stress Equations and Calculator. Is the total heat exchanger surface area.
Parallel and Counter-Flow Designs Parallel and Counter Flow heat exchanger Designs. The mean temperature difference in a heat transfer process depends on the direction of fluid flows involved in the process. The transport equations for thermal energy Fouriers law mechanical momentum.
Air stream The T-Q diagram is 1200. The use of Equations 2-4 and 2-5 in determining the amount of heat transferred by conduction is demonstrated in the following examples. Non-Regenerative Heat Exchanger The non-regenerative application is the most frequent and involves two separate fluids.
And in cross flow the fluids move at right angles to each other. Shear Stress in Shafts Calculator. Common types of heat exchanger flows include parallel flow counter flow and cross flow.
Statics Force Analysis for Cylinder Supported by Two Rollers Equation and Calculator. Spiral flow passages are welded at each side for this type of spiral heat exchanger. In the parallel-flow arrangement of Figure 188a the hot and cold fluids enter at the same end flow in the same direction and leave at the same end.
To solve complex flow equations highly accurate meshing and geometries are needed to provide input for efficient numerical methods. Do not change in time. In the following figure you can see the curves to find the effectiveness of a cross flow heat exchanger for different values of NTU and C r.
PDF A heat exchanger is a heat transfer device that exchanges heat between two or more process fluids.

Understanding Heat Exchangers Types Designs Applications And Selection Guide

Chapter 3 2 Heat Exchanger Analysis Using Ntu Method Ppt Video Online Download

Comments
Post a Comment